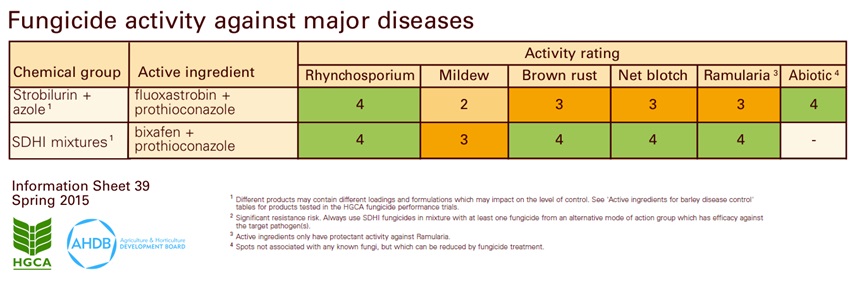
Cultural Control
Target:
Pre-drilling, rotational strategies
Key aim:
Reduce the levels of the disease in a crop by using an integrated strategy involving varietal resistance, controlling the green bridge, drilling date and trash burial.
Varietal resistance:
Planting varieties which are less susceptible to diseases can significantly diminish the levels of infection. Resistant varieties are best used in circumstances where disease risk is higher i.e. earlier drilled crops. Be careful to select a variety which has good resistance to the most prevalent diseases in your area. The graph below shows how a resistant variety, used in combination with a fungicide programme, can increase the return on investment of fungicides.
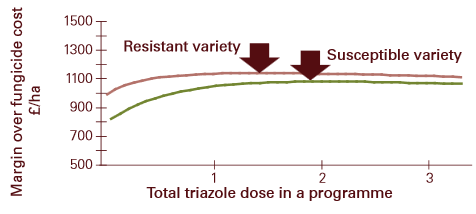
Source: HGCA Barley disease management guide 2014
Controlling the green bridge:
Barley brown rust and powdery mildew both overwinter on volunteers. Ensure that volunteers are sprayed off on overwintered stubbles to control the inoculum levels in following and nearby crops
Drilling date:
Although planting crops earlier may increase the chance of maximising the yield it will significantly risk of disease epidemics. If you are planning to drill early then consider offsetting the increased risk by choosing a variety with good resistance.
Cultivations:
Spores fromboth Rynchosporium and net blotch over winter on trash from the previous crop. If growing a crop adjacent to or after a previous barley crop then consider burying the trash by ploughing.
Benefits:
Controlling disease as part of an integrated crop management approach, using both cultural and chemical control, will reduce the overall levels of infection and maximise yields.