

Batavia
Batavia is a new two-way systemic ketoenol insecticide to control sucking pests in top fruit and selected soft-fruit crops.
Product details
It's becoming increasingly hard to keep on top of sucking pest problems in fruit. This can lead to crop rejection or reduction in value, hitting your profit margins.
Batavia fills the gap with an active substance that's new to UK fruit growers, yet is proven in European and UK vegetable crops.
Applied in the early stages of pest migration and colonisation, it gives thorough population control of a range of sucking pest species. Batavia is particularly recommended against aphids but is also active against pests like apple scale, making it highly cost-effective.
Ensure maximum marketable quality and yield. Rely on Batavia to do the heavy lifting in sucking pest control.
Summary
Crop-specific pests and use
*Under certain circumstances fruit trees may exhibit symptoms of leaf scorch following applications of Batavia. When applying Batavia to fruit trees, ensure that the trees are not under stress, for example nutrient or water deficiency.
Spirotetramat, the active substance in Batavia, offers a unique combination of attributes.
Protects the whole plant: two-way systemicity
Typical systemic insecticides, such as thiacloprid, are transported in the xylem only – outwards and upwards from the point of application: they are one-way systemic.
Spirotetramat is additionally transported in the phloem, and so can move back down into the plant and towards new growth; this makes it two-way systemic.
As a result, Batavia not only controls hidden and hard-to-target pests, but delivers unrivalled protection of new growth. Sucking pests merely have to ingest spirotetramat while actively feeding to ensure control.

As well as being transported in the xylem, spirotetramat moves via the phloem towards new growth
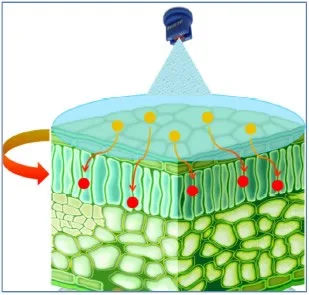
After being sprayed on the leaf, inactive spirotetramat is converted to spirotetramat cis-enol, which is active and highly mobile in xylem and phloem
Gives thorough, lasting control: lifecycle disruption
Batavia’s MoA breaks the lifecycle – and is therefore highly effective in reducing pest populations and avoiding bounce-back.
Insects rely heavily on lipids (fats and similar substances) for their metabolic needs, particularly to aid reproduction, embryogenesis (formation and development of young), metamorphosis and moulting (moving from one growth stage to another) and flight.
Spirotetramat inhibits acetyl CoA carboxylase (ACC-ase), which in turn inhibits lipid biosynthesis. This offers very powerful opportunities for control. Young insects cannot mature, leading to lack of fecundity and fertility. Eggs fail to hatch. Larvae fail to develop. Moults are incomplete. Adult females accumulate nymphs and die.

Strong effects on fecundity and fertility;
failed egg hatch and poor larval development

Incomplete moulting and subsequent death

Females deposit non-viable nymphs of e.g. aphids
Batavia has been shown to give clear results against aphids and other sucking pests on a range of varieties and in different situations.
Broad-spectrum sucking pest control in apples
BEL 2010 Cv Jonagold

A single application of Batavia provides stronger control consistently against key pests compared to standard treatments. Note: pirimicarb is no longer authorised in this crop in the UK
EAMU – Woolly apple aphid
This EAMU relates to the use of Batavia on outdoor apple for the control of woolly apple aphid (Eriosoma lanigerum).
Applications must be made via broadcast air-assisted sprayers in a water volume of 500-1,500 L/ha from May, starting at BBCH 69 (end of flowering) to September, at BBCH 81 (beginning of ripening).
An aquatic buffer zone of 15 metres must be observed.
* An interval of 14 days between applications is applicable.

The best time for application is when the young are moving to the new shoots.
The product dose should be reduced for smaller trees as follows:
* Crop Canopy Height (CH) is the average tree height in the orchard (soil to the top of the crown) minus the average trunk height in the orchard (soil to first main branch).
Good efficacy can be expected on trees with a crop canopy height of up to 2.4m. On trees taller than this, control could become more variable with slower initial efficacy, or lower efficacy overall.
Sucking pest in apples, pears, cherries, plums and strawberries
Optimal timing is critical to get the most from Batavia.
In principle, use from BBCH 69 (post-flowering) up to BBCH 81 (onset of maturity phase) in outdoor apple, pear, cherry and plum – in other words, when there is sufficient leaf area and active growth for good movement of sap in the redistributive phloem.

Due to the mode of action, don't expect rapid knock-down of pests. Obvious control usually occurs after 3-7 days and depends on the pest stage – the youngest larvae are the most susceptible and adults least susceptible.
This is why timing of the first application is key – too early, and the active substance will run out of steam; too late and populations will have become established, making control more difficult.
Don't forget that there are two situations to consider:
Sucking pests that mainly remain in the orchard and over-winter (e.g. mussel scales/woolly apple aphid). Apply Batavia when pests start to migrate towards the new growth to feed and reproduce.
Migratory sucking pests that tend to over-winter elsewhere and arrive in the orchard during the season. Time applications of Batavia in the early stages of infestation to prevent population build-up before large colonies develop.
Repeat application after a minimum of 14 days if you need further control, and ensure you use alternative MoAs within your insecticide programme. To be certain of timing, however, consult your advisor. You can also contact the fruit specialists in our horticulture team.

Time first application at early migration of over-wintering sucking pests from old wood to new shoots
Stress factors
Before you apply Batavia, consider factors that limit tree growth or movement of sap in the phloem and could suppress uptake and redistribution of spirotetramat through the plant's vascular system. These include some growth regulators, some thinners, root pruning, extensive drought or heat. Consult your advisor.
Use in programmes
As spirotetramat is a tetramic acid derivative with a similar mode of action to spirodiclofen, it belongs to Group 23 within the IRAC Mode of Action Classification scheme (www.irac-online.org).
If you rely exclusively on one pesticide, this will hasten the development of resistance; you should therefore include pesticides of different chemical types or alternative control measures in a planned programme.
Use Batavia in a spray programme with other insecticides of a different mode of action, in alternation or as a two-spray block, respecting a minimum 14 day interval.
Always apply Batavia at the full recommended rate of use for the crop canopy size (see below) and target pest, and in sufficient water volume to achieve the required spray penetration.
Be sure to respect a minimum 21-day PHI (post-harvest interval).
Tailored dose
Like many products for top fruit, Batavia allows you to adapt application according to the crop canopy height. A variable dose may both help reduce your spray costs and contribute to responsible stewardship.

Max. individual dose 1.5 L/ha – but apply variable dose according to crop canopy height
Bayer trials, 190 results